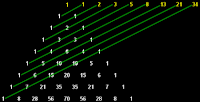
Codigo Fuente en Replit
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
//#define n 5
int menu();
int M[20][20];int x,y,d,n;
int mat[20][20],i,j,c=0;
void pascal4()
{
int M[20][20],x,y,d;
cout<<"Ingrese la dimension de la matriz:";
std::cin>>d;
for(x=1;x<=d;x++)
for (y=1;y<=d;y++)
M[x][y]=0;
for (x=1;x<=d;x++)
M[x][d]=M[x][d+1-x]=1;
for (x=3;x<=d;x++)
for (y=d-1;y>=d+2-x;y--)
M[x][y]=M[x-1][y+1]+M[x-1][y];
for (x=1;x<=d;x++) {
for (y=1;y<=d;y++) {
if(M[x][y]==0)
cout<<" ";
else
if (M[x][y]<=9)
cout<<" "<<M[x][y];
else
cout<<" "<<M[x][y];
}
cout<<"\n";
}
}
void pascal3()
{
int M[20][20],x,y,d;
system("cls");
cout<<"TRIANGULO DE PASCAL # 3";
cout<<"";
cout<<"\nIngrese la dimension de la matriz:";
cin>>d;
for(x=1;x<=d;x++)
for (y=1;y<=d;y++)
M[x][y]=0;
for (x=1;x<=d;x++)
M[1][x]=M[x][d+1-x]=1;
for (y=d-2;y>=1;y--)
for (x=2;x<=d-y;x++)
M[x][y]=M[x-1][y+1]+M[x][y+1];
for(x=1;x<=d;x++){
cout<<"\n\t";
for (y=1;y<=d;y++){
if(M[x][y]==0)
cout<<" ";
else
if (M[x][y]<=9)
cout<<" "<<M[x][y];
else
cout<<" "<<M[x][y];
}
}
}
void pascal2()
{
cout<<"TRIANGULO DE PASCAL 2";
int X,Y,calderon,d;
int A[20][20];
{
cout<<" \n";
cout<<"Digite dimension de la matriz:";
cin>>d;
cout<<" \n\n";
for(X=1;X<=d;X++)
{
A[1][X]=1;
A[X][X]=1;
}
for(Y=3;Y<=d;Y++)
{
for(X=2;X<=Y-1;X++)
A[X][Y]= A[X][Y-1] + A[X-1][Y-1];
}
cout<<" \n\n";
cout<<"********* TRIANGULO DE PASCAL # 2 ********:\n";
cout<<" \n\n";
for(X=1;X<=d;X++)
{
for(Y=1;Y<=X-1;Y++) cout<<" ";
for(Y=X;Y<=d;Y++)
{
cout<<" "<<A[X][Y];
}
cout<<" \n";
}
}
}
void pascal6(){
cout<<"\nTRIANGULO DE PASCAL #6......";
cout<<"\nDigite la dimencion...N=";
std::cin>>n;
d=n;
for(x=1;x<=d;x++) for(y=1;y<=d;y++) M[x][y]=0;
for(x=1;x<=d;x++) M[d][x]=M[x][x]=1;
for (y=d-2;y>=1;y--)for (x=d-1;x>=y+1;x--) M[x][y]=M[x+1][y+1]+M[x][y+1];
for(x=1;x<=d;x++){cout<<"\n";for(y=1;y<=d;y++) {if(M[x][y]==0) cout<<" ";
else
cout<<M[x][y]<<"\t";}}
}
void pascal5(){
int n;
cout<<"\nTRIANGULO DE PASCAL # 5.......=";
cout<<"\nDigite la dimencion...N=";
std::cin>>n;
//cinn;
for(x=1;x<=n;x++) for (y=1;y<=n;y++) mat[x][y]=0;
for (x=1;x<=n;x++)mat[1][x]=mat[x][n+1-x]=1;
for (y=n-2;y>=1;y--)for (x=2;x<=n-y;x++)
mat[x][y]=mat[x-1][y+1]+mat[x][y+1];
cout<<"\n\n";
for(i=1;i<=n;i++){for(j=1;j<=n;j++){if (mat[j][i]==0)j=n;
printf("%d\t",mat[j][i]);}
printf("\n");
}
}
void pascal1()
{
int x,y,dimen;
int mat[20][20],fil=2,col=2;
printf("Digite la dimencion:");
scanf("%d",&dimen);
printf("\n\n");
for(x=1;x<=dimen;x++)
{
mat[x][1]=1;
mat[x][x]=1;
}
for(x=3;x<=dimen;x++)
{
for(y=2;y<=x-1;y++)
mat[x][y]=mat[x-1][y]+mat[x-1][y-1];
}
for(x=1;x<=dimen;x++)
{
for(y=1;y<=x;y++)
{
printf("%d ",mat[x][y]);
;
col=col+5;
}
fil=fil+1;
printf("\n");
col=2;
}
}
int main(){
int salir=0;
do {
switch(menu()){
case 1:
pascal1();
break;
case 2:
pascal2();
break;
case 3:
pascal3();
break;
case 4:
pascal4();
break;
case 5:
pascal5();
break;
case 6:
pascal6();
break;
case 0:
salir=0;
break;
default:
printf("Opcion No Valida.");
break;
}
}while(salir!=0);
}
int menu(){
int opc;
printf("\n\t\t_______________________________________");
printf("\n\n\t\t -=TRIANGULOS DE PASCAL=- \n\n\n");
printf("\t\t1) Pascal. 4) Pascal 4.\n\n");
printf("\t\t2) Pascal. 5) Pascal 5.\n\n");
printf("\t\t3) Pascal 6) Pascal 6.\n\n");
printf("\t\t0) Salir.\n\n\t\tMetodo a Utilizar: ");
std::cin>>opc;
printf("\t\t_________________________________________\n");
return(opc);
printf("\n\n");
}
MULTIPLICACIÓN DE MATRICES
Codigo fuente en C++ FACTORIAL DE UN NUMERO
#include <iostream>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
{
if(n<2)
return 1;
else
return n * factorial(n-1);
}
int combinacion(int n, int r)
{
if(r==1)
return n;
else
{
if(n==r)
return 1;
else
return factorial(n) / (factorial(r) * factorial(n - r));
}
}
int main()
{
for(int i=0; i<=6; i++)
{
for(int ii=0; ii<=i; ii++)
cout << combinacion(i, ii) << " ";
cout << endl;
}
return 0;
}
No hay comentarios:
Publicar un comentario